The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is a smart way to manage your stock. It helps you order just enough to avoid extra costs from ordering too much, storing it, or running out.
EOQ cuts down on storage fees like rent and insurance, and helps you save on costs every time you place an order by buying more at once. It makes handling inventory simpler and helps you predict spending better.
Want to save money and manage your stock more easily? Keep reading to find out how EOQ can help.
How Economic Order Quantity Helps Streamline Inventory Management
The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) formula is the cornerstone of effective inventory management, calculating the optimal order quantity to minimize the total inventory costs.
What is Economic Order Quantity?
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is your go-to calculation for identifying the most cost-effective quantity of inventory to order. It represents the ideal amount of stock that your business should order to minimize costs associated with buying, delivering, and storing products.
The EOQ addresses the challenge of determining the optimal order quantity that contributes the least to total costs concerning inventory.
Also read: How to Manage E-commerce Backorders and Inventory Replenishment (Tips and Best Practices)
Advantages of Economic Order Quantity in Minimizing Costs
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is a critical tool in inventory management, offering substantial cost benefits. By calculating the ideal order quantity, your business can achieve a balance between various costs associated with inventory.
Reduced Holding Costs: EOQ helps you avoid excessive inventory, which ties up capital. By holding only the stock you need, you save on storage space, minimize the risk of obsolescence, and improve cash flow since less money is bound up in unsold goods.
Lower Order Costs: When you order in bulk, you often enjoy reduced prices and shipping efficiencies.
Improved Cash Flow: Managing your cash flow effectively means having money on hand for other areas of your business. EOQ aids in predicting when to reorder and how much, preventing unnecessary capital lockup in inventory.
Optimized Inventory Turnover: A well-implemented EOQ results in faster turnover rates, ensuring your stock is sold before becoming outdated or before the costs of holding it surpass its value.
Prevention of Stockouts: Running out of inventory can be costly – both in terms of lost sales and damaged reputation. EOQ calculates an optimal reorder point to prevent stockouts.
Quantity Discounts: EOQ can also inform your purchase decisions to capitalize on quantity discounts without causing overstock. By purchasing the optimal amount of inventory, you take advantage of purchase discounts while dodging the pitfalls of excess inventory.
Increase Customer Satisfaction: An effective EOQ reduces the chances of running out of stock, meaning you’re more likely to fulfill customer orders promptly. Timely order fulfillment generally increases customer satisfaction, as your clients receive their products without unnecessary delays.
Benefit | Impact on Your Business |
Minimize Costs | Direct savings on inventory-related expenses |
Inventory Management | Streamlined operations lead to efficiency gains |
Cash Flow | Better liquidity with optimized stock levels |
Storage Cost | Lower expenses due to reduced space requirements |
Disadvantages of Economic Order Quantity
While Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) can help minimize storage and ordering costs, it also comes with a set of drawbacks that you should consider. These challenges can impact the efficacy of the inventory management technique.
Complex Mathematical Calculations
EOQ involves intricate formulas to determine the ideal order quantity.
You need to be skilled in calculating square roots and working with other mathematical models, which might require specialized software or personnel.
This complexity can be a major hurdle if you prefer a more straightforward approach to managing your inventory.
Assumptions and Limitations
The effectiveness of EOQ hinges on certain assumptions that may not hold true for all businesses.
It assumes a constant demand for products and a constant demand rate, which is rarely the case in a dynamic market environment.
Moreover, fluctuations in market conditions or in the cost of items can render EOQ calculations inaccurate, thereby limiting its applicability and potential benefits.
Factors You Need to Analyze EOQ
When determining the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) for your inventory, understanding the interplay between holding costs, ordering costs, and annual demand is crucial.
Precise calculation of these factors is key for optimizing your inventory levels and reducing overall costs.
Holding Costs (H)
Holding costs (H), often referred to as carrying or storage costs, encompass expenses associated with storing unsold inventory. These costs include:
Warehouse storage expenses: These could be the rent or depreciation of storage space.
Insurance and taxes: Recurring costs to protect and legitimize the stored products.
Opportunity cost of capital: The potential of return from the investment tied up in the inventory.
Spoilage or obsolescence: Costs incurred from unsellable inventory due to expiration or irrelevance.
It's vital that you track these costs per unit to ascertain the financial impact of maintaining inventory levels.
Ordering Costs (S)
Ordering costs (S), or setup costs, are the expenses incurred each time an order is placed, regardless of the order's size. These can include:
Supplier communication expenses: The operational cost of negotiating and processing with suppliers.
Shipping and handling fees: Charges related to the physical movement of goods.
Administrative costs: Staff time and resources spent on order management and processing.
Understanding EOQ is enhanced by comprehensive inventory reports, which track and analyze stock performance. Learn more about them here: The Power of an Amazon Inventory Report
How To Calculate Economic Order Quantity
In managing your inventory effectively, calculating the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is a vital step to minimize inventory costs. These costs include ordering, holding, and shortage costs.
Factors to Optimize Inventory
To calculate EOQ, you need to consider three main cost factors that influence your inventory levels:
Demand Rate (D): This is the number of units you expect to sell over the course of a year. It sets the baseline for how much inventory you need.
Setup Costs (S): Also referred to as order costs. These are the costs associated with placing and receiving orders, such as shipping fees and labor. They occur every time an order is placed and can decrease with larger, less frequent orders.
Holding Costs (H): These costs, incurred for storing inventory, can include warehouse rent, insurance, and spoilage risk. They usually increase with higher inventory levels.
EOQ is found at the point where ordering costs and holding costs are balanced, leading to the lowest total inventory cost. To calculate EOQ, use the square root formula:
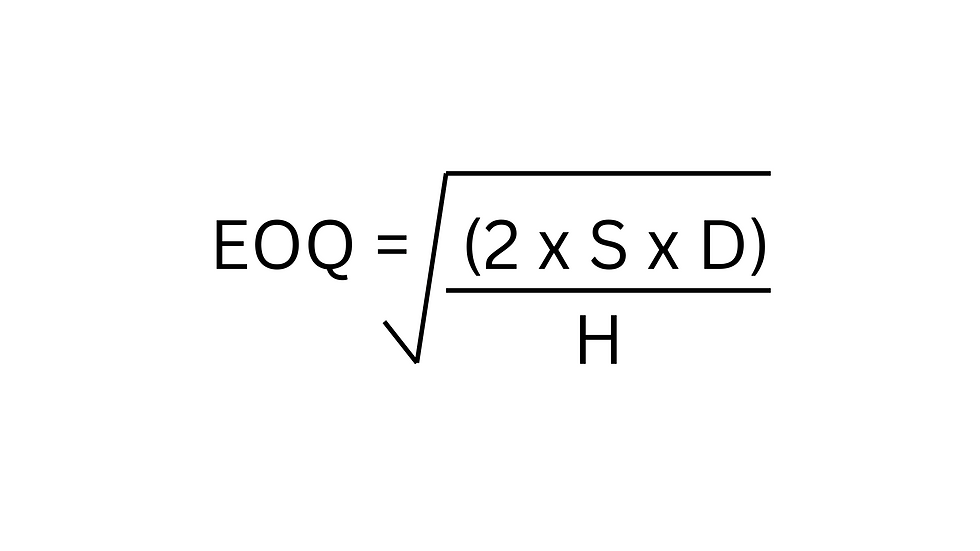
By striking the right balance and calculating the EOQ, you can optimize your inventory to function at peak efficiency with minimized costs.
Example
Suppose your annual demand for a product is 1,000 units, the cost per order is $50, and the holding cost per unit per year is $5. You can calculate the EOQ as follows:
EOQ = √((2 x Annual Demand x Ordering Cost) / Holding Cost)
EOQ = √((2 x 1,000 units x $50) / $5)
EOQ = √(100,000 / 5)
EOQ = √20,000
EOQ = 141.42
Thus, you should order approximately 141 units each time to achieve the lowest total cost in managing your inventory.
Conclusion
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is a powerful tool for efficient inventory management, helping businesses minimize costs and optimize stock levels.
By accurately determining order sizes, EOQ ensures a balance that prevents stock shortages and excess, improves cash flow, and accelerates inventory turnover. Integrating EOQ into business operations promotes financial savvy and operational success in a competitive environment.
EOQ stands out for its straightforward approach to reducing inventory costs, supporting companies in boosting profitability. Its strategic use enhances the consistency of supply, customer satisfaction, and enables informed, data-based decisions.
3PL services help you manage stock better by lowering storage costs and improving how you track inventory, making it easier to know when to reorder. Our services can make your EOQ even more accurate, saving you money and keeping your stock moving. Get in touch to improve your inventory system with our help.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is EOQ important in inventory management?
EOQ is crucial in inventory management because it helps determine the most cost-effective amount of stock to order. This optimal quantity minimizes the total costs of holding inventory and ordering it, which can include storage, insurance, and purchase order processing.
By using EOQ, businesses can avoid excess inventory that ties up capital and increases storage costs, as well as reduce the risk of stockouts that can lead to lost sales. It's a key figure for maintaining an efficient, cost-controlled inventory system.
Are EOQ and MOQ the same?
No, EOQ (Economic Order Quantity) and MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) are not the same. EOQ is a calculation businesses use to determine the ideal number of items they should order to minimize costs related to inventory, such as holding, ordering, and shortage costs.
MOQ, on the other hand, is the minimum quantity a supplier is willing to sell. It's set by suppliers to ensure that they cover production costs and is not tailored to the buyer's cost-minimization strategy like EOQ is.
Related article: What is an MOQ? Minimum Order Quantities Explained
Do you round up for EOQ?
Yes, you typically round up when calculating EOQ. Since it's not usually feasible to order a fraction of a product, you round the EOQ to the nearest whole number.
However, it's important to consider business constraints and rules—for example, if products are only available to order in batches or multiples, you'll need to round up to the nearest batch size or multiple that fulfills the EOQ requirement.
What is the difference between EOQ and order quantity?
EOQ refers to the most cost-effective quantity to order, taking into account various inventory-related costs. In contrast, 'order quantity' can refer to any quantity of goods a company decides to order at a particular time, which may or may not be the economical or optimal amount.
While EOQ aims to minimize costs and maximize efficiency, the actual order quantity a business uses could be influenced by other factors, like supplier constraints, seasonal demand, or purchasing budget limits.


Comments